🧩 Deployment Process Automater! -- Ansible x Terraform to Automate Deployment Process.

UNLIMITED POWER
I- Intro
Integrating AWS, Ansible, Terraform, and Docker-Compose provides a powerful framework for managing cloud infrastructure and deploying applications.
By leveraging the strengths of each tool, organizations can streamline their workflows, improve consistency, and enhance scalability. This combination is essential for modern DevOps practices and cloud-native application development.
To create a fully automated workflow using AWS, Terraform, Ansible, and Docker-Compose, follow these steps:
1. Provision Infrastructure with Terraform: Use Terraform to create the necessary AWS resources, such as EC2 instances and security groups.
2. Configure Instances with Ansible: Once the infrastructure is provisioned, use Ansible to install required software (like Docker) and configure the instances.
3. Deploy Applications with Docker-Compose: Finally, use Docker-Compose to deploy your application containers on the configured instances.
By combining these tools, you can achieve a robust and automated deployment pipeline that enhances productivity and reduces the risk of errors.
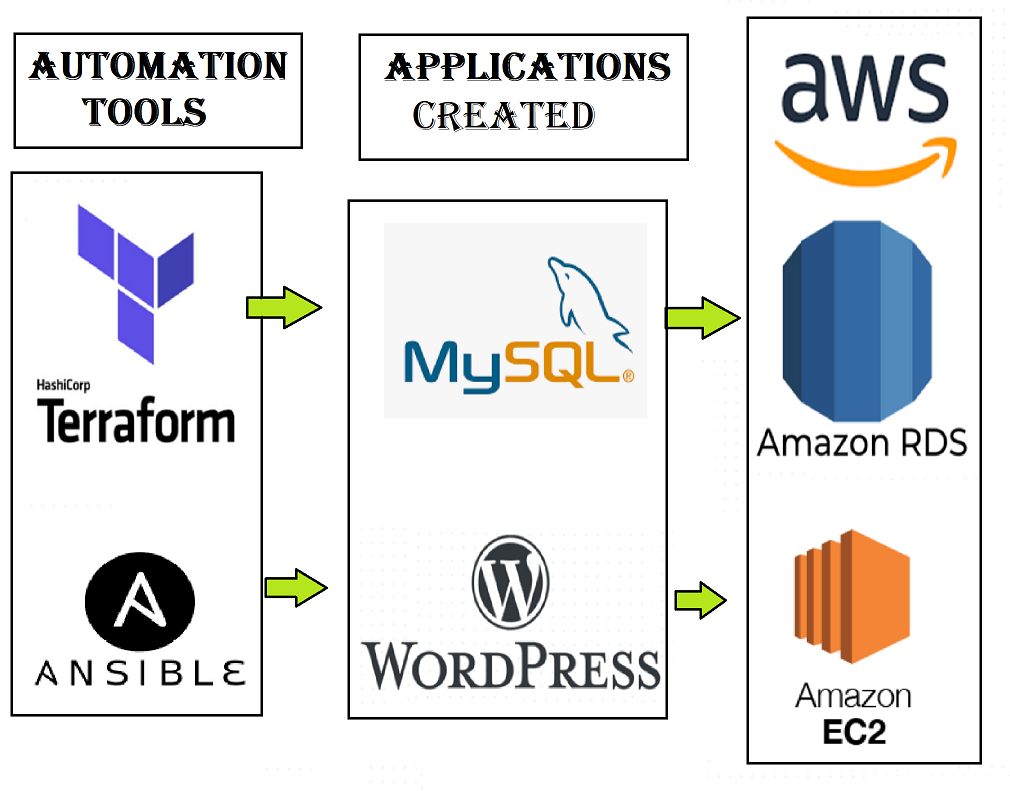
design example of the process
II - Implementation
1- Ansible: Playbooks Configuration management.
setup.yml config to setup the new created EC2 instances with useful tools and dependencies such as docker and others.
---
- name: Install Docker on EC2
hosts: ec2
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install required packages
apt:
name:
- apt-transport-https
- ca-certificates
- curl
- gnupg
- lsb-release
state: present
update_cache: true
- name: Add Docker's official GPG key
apt_key:
url: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg
state: present
- name: Add Docker repository
apt_repository:
repo: "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu\
{{ ansible_distribution_release | lower }} stable"
state: present
- name: Add user to docker group
user:
name: ubuntu
groups: docker
append: yes
- name: Install Docker Engine
apt:
name: docker-ce
state: latest
update_cache: yes
- name: Ensure Docker service is started and enabled
service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Install Docker Compose
get_url:
url : https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.25.1-rc1/docker-compose-Linux-x86_64
dest: /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
mode: 'u+x'
deploy.yml config to automatically deploy our app on the EC2 instances.
---
- name: Deploy WordPress with Docker Compose
hosts: ec2
become: yes
vars:
project_dir: /home/ubuntu/cloud-1
tasks:
- name: Create project directory
file:
path: "{{ project_dir }}"
state: directory
owner: ubuntu
group: ubuntu
mode: '0755'
- name: Copy docker-compose.yml to EC2 instance
copy:
src: ../srcs/docker-compose.yml
dest: "{{ project_dir }}/docker-compose.yml"
owner: ubuntu
group: ubuntu
mode: '0644'
- name: Copy docker-compose.yml to EC2 instance
copy:
src: ../srcs/docker-compose.yml
dest: "{{ project_dir }}/docker-compose.yml"
owner: ubuntu
group: ubuntu
mode: '0644'
- name: Copy .env file to EC2 instance
copy:
src: ../srcs/.env
dest: "{{ project_dir }}/.env"
owner: ubuntu
group: ubuntu
mode: '0644'
- name: Deploy Docker Compose stack
community.docker.docker_compose_v2:
project_src: "{{ project_dir }}"
state: present
2- Docker-Compose: Containers setup.
docker-compose.yml code to create docker container that will be deployed as our app.
version: '3.9'
services:
db:
image: mysql:latest
container_name: db
restart: unless-stopped
env_file: .env
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: ${MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD}
MYSQL_USER: ${MYSQL_USER}
MYSQL_PASSWORD: ${MYSQL_PASSWORD}
MYSQL_DATABASE: ${MYSQL_DATABASE}
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
networks:
- cloud-1
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "mysqladmin", "ping", "-h", "localhost"]
interval: 5s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
wordpress:
depends_on:
db:
condition: service_healthy
image: wordpress:latest
container_name: wordpress
restart: unless-stopped
env_file: .env
environment:
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: ${WP_DB_HOST}
WORDPRESS_DB_USER: ${WP_ADMIN_USER}
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: ${WP_ADMIN_PASS}
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME: ${MYSQL_DATABASE}
ports:
- "9000:80"
volumes:
- wp_data:/var/www/html
networks:
- cloud-1
phpmyadmin:
depends_on:
db:
condition: service_healthy
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin:latest
container_name: phpmyadmin
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "8180:80"
env_file: .env
environment:
PMA_HOST: ${DB_HOST}
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: ${PHPMYADMIN_PASSWORD}
networks:
- cloud-1
volumes:
db_data:
driver: local
wp_data:
driver: local
networks:
cloud-1:
driver: bridge
3- Automation Script: Automation code.
main.go code to automate the creation of AWS EC2 instances using Terraform, and applying Ansible playbooks to them.
func runAnsiblePlaybook(playbookPath string, inventoryPath string) error {
cmd := exec.Command("ansible-playbook", "-i", inventoryPath, playbookPath)
cmd.Stdout = os.Stdout
cmd.Stderr = os.Stderr
cmd.Stdin = os.Stdin
return cmd.Run()
}
func writeInventoryFile(ips []string, path string) error {
var sb strings.Builder
sb.WriteString("[ec2]\n")
ansible_ssh_private_key_file := os.Getenv("ANSIBLE_SSH_PRIVATE_KEY_FILE")
ansible_user := os.Getenv("ANSIBLE_USER")
for _, ip := range ips {
sb.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("%s ansible_user=%s \
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=%s\n", ip, ansible_user,\
ansible_ssh_private_key_file))
}
return os.WriteFile(path, []byte(sb.String()), 0644)
}
func getInstanceIPsFromState(stateFilePath string) ([]string, error) {
data, err := os.ReadFile(stateFilePath)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to read state file: %w", err)
}
var tfState map[string]interface{}
if err := json.Unmarshal(data, &tfState); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to parse JSON: %w", err)
}
resources, ok := tfState["resources"].([]interface{})
if !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unexpected structure\
in state file: resources not found")
}
var ips []string
for _, res := range resources {
resource, ok := res.(map[string]interface{})
if !ok || resource["type"] != "aws_instance" {
continue
}
instances, ok := resource["instances"].([]interface{})
if !ok {
continue
}
for _, inst := range instances {
instance, ok := inst.(map[string]interface{})
if !ok {
continue
}
attr := instance["attributes"].(map[string]interface{})
ip, ok := attr["public_ip"].(string)
if ok && ip != "" {
ips = append(ips, ip)
}
}
}
if len(ips) == 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("no public IPs found")
}
return ips, nil
}
Ansible Playbooks automation
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"os/exec"
"path/filepath"
"github.com/joho/godotenv"
"strings"
"encoding/json"
)
func runCommand(args ...string) error {
cmd := exec.Command("terraform", args...)
cmd.Stdout = os.Stdout
cmd.Stderr = os.Stderr
cmd.Stdin = os.Stdin
return cmd.Run()
}
func runTerraformApply() {
err := os.Chdir("./terraform")
if err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println("Initializing Terraform...")
if err := runCommand("init"); err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println("Planning Terraform...")
if err := runCommand("plan"); err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println("Applying Terraform...")
if err := runCommand("apply", "-auto-approve"); err != nil {
return
}
}
func main() {
err := os.MkdirAll("terraform", 0755)
if err != nil {
return
}
// Load environment variables from .env
err = godotenv.Load("../.env")
if err != nil {
return
}
accessKey := os.Getenv("AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID")
secretKey := os.Getenv("AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY")
ami := os.Getenv("AWS_AMI")
keyName := os.Getenv("AWS_KEY_NAME")
// Generate the Terraform file
content := fmt.Sprintf(`
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
access_key = "%s"
secret_key = "%s"
}
resource "aws_instance" "cloud-1" {
ami = "%s"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "%s"
security_groups = ["terraform_sg"]
count = 2
tags = {
Name = "server"
}
}
resource "aws_security_group" "terraform_sg" {
name = "terraform_sg"
description = "Allow SSH, HTTP, HTTPS, and all outbound traffic"
ingress {
description = "SSH"
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
ingress {
description = "TCP"
from_port = 8000
to_port = 9999
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
description = "Allow all outbound"
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
`, accessKey, secretKey, ami, keyName)
tfPath := filepath.Join("terraform", "main.tf")
err = os.WriteFile(tfPath, []byte(content), 0644)
if err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println("Terraform file written: terraform/main.tf")
runTerraformApply()
ips, err := getInstanceIPsFromState("../terraform/terraform.tfstate")
if err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println("Public IPs:", ips)
if err := writeInventoryFile(ips, "../ansible/inventory/inventory.ini"); err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println("Running Ansible Setup Playbook...")
if err := runAnsiblePlaybook("../ansible/playbooks/setup.yml", \
"../ansible/inventory/inventory.ini"); err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println("Running Ansible Deploy Playbook...")
if err := runAnsiblePlaybook("../ansible/playbooks/deploy.yml", \
"../ansible/inventory/inventory.ini"); err != nil {
return
}
}
IaC with Terraform automation.
🚀 By following these steps, we should be able to have our app display a custom page at http://localhost:9000.